Various test methods for characterizing and testing materials are available in the fire test laboratory:
In the course of the increasing electrification of components, the material property of tracking resistance is particularly important in the electronics and automotive industries as well as other applications with high voltages. A high tracking resistance means that a material has a better insulation capacity under the influence of moisture and dirt and thus enables improved reliability and safety of electrical systems.
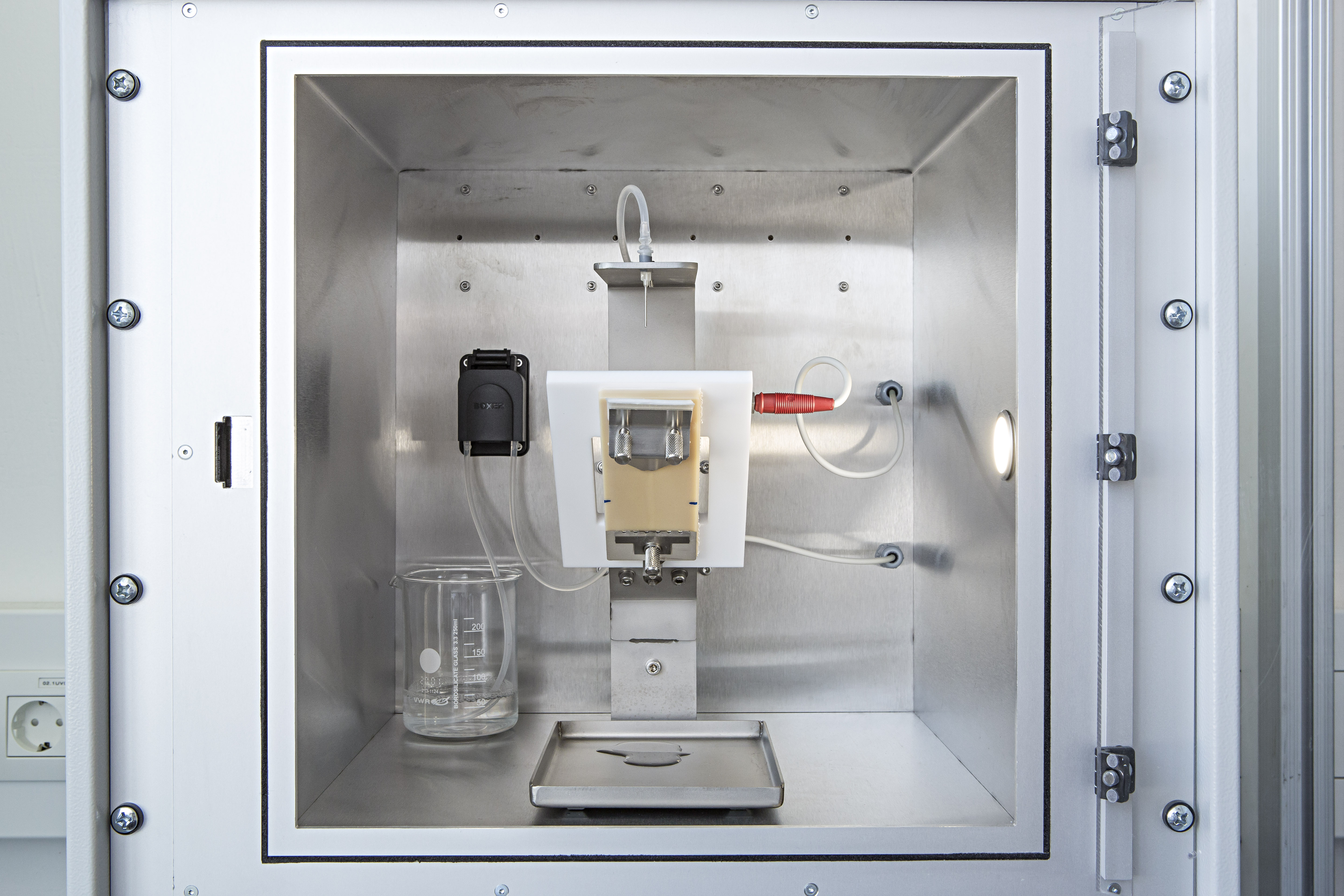
The tracking resistance (Comparative Tracking Index, CTI) of insulating materials can be determined using the method according to DIN EN 60112. During the test, a sample (≥ 20 mm x ≥ 20 mm x ≥ 3 mm) is placed between two electrodes and subjected to a gradually increasing voltage while a conductive liquid is dripped onto the surface at a defined time interval. The liquid forms a conductive bridge between the electrodes.
The CTI value is the maximum voltage at which 5 samples can withstand 50 drops without creepage or sustained flame. A higher CTI value means better resistance to leakage currents.

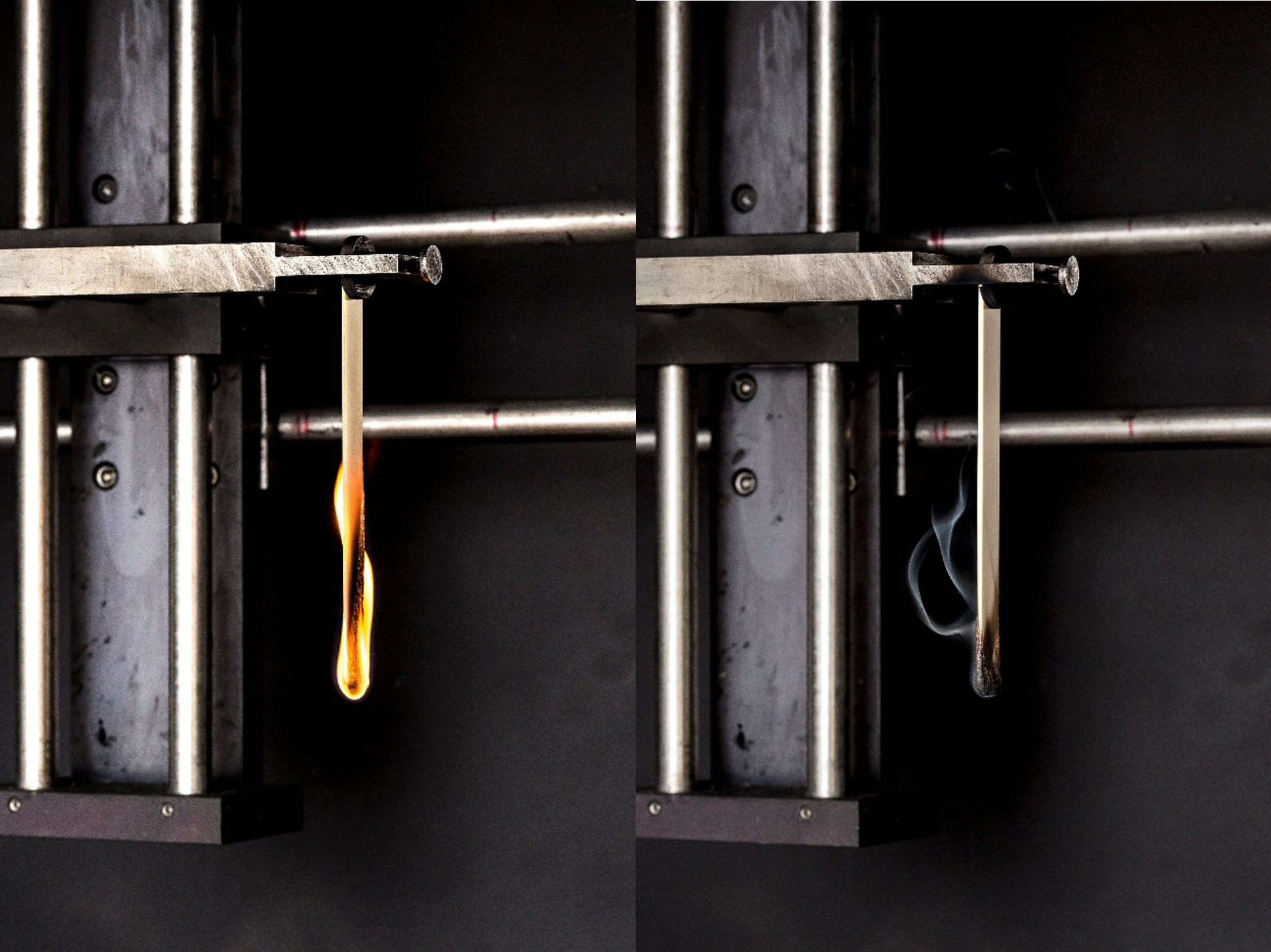
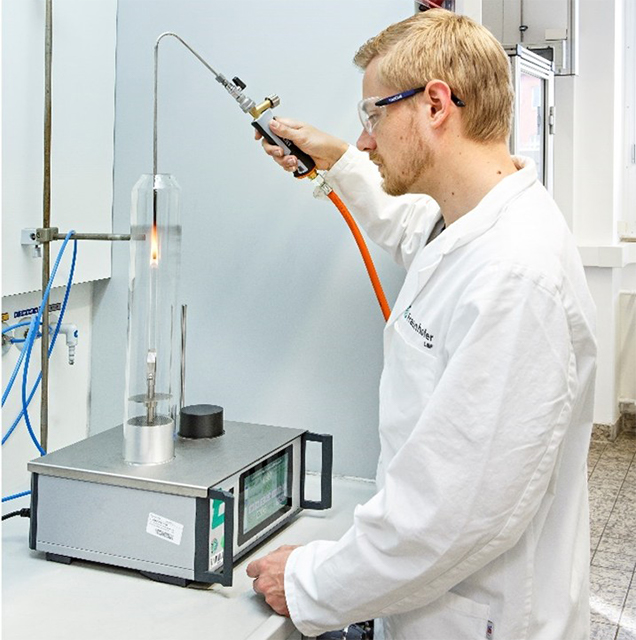
Fire safety for electrical appliances places high demands on the glow wire resistance of non-metallic materials used in unattended appliances. The glow wire simulates a potential ignition source in electrical devices and the temperature of the wire is gradually increased until the sample ignites.
The GWIT (glow wire ignition temperature) can be used to determine the flammability of materials through contact with a glow wire, whereby the GWIT corresponds to the minimum temperature value at which the material ignites and burns for > 5 s in three consecutive tests.

The limiting oxygen index (LOI) corresponds to the minimum oxygen concentration required for a material to still show combustion with the appearance of a flame under defined conditions. The sample is ignited in a controlled atmosphere with a defined concentration of oxygen in nitrogen. The oxygen concentration is gradually changed until the minimum concentration can be determined that the sample needs in order to just burn. A higher oxygen volume fraction and thus a higher LOI value correspond to improved flame resistance of the material.

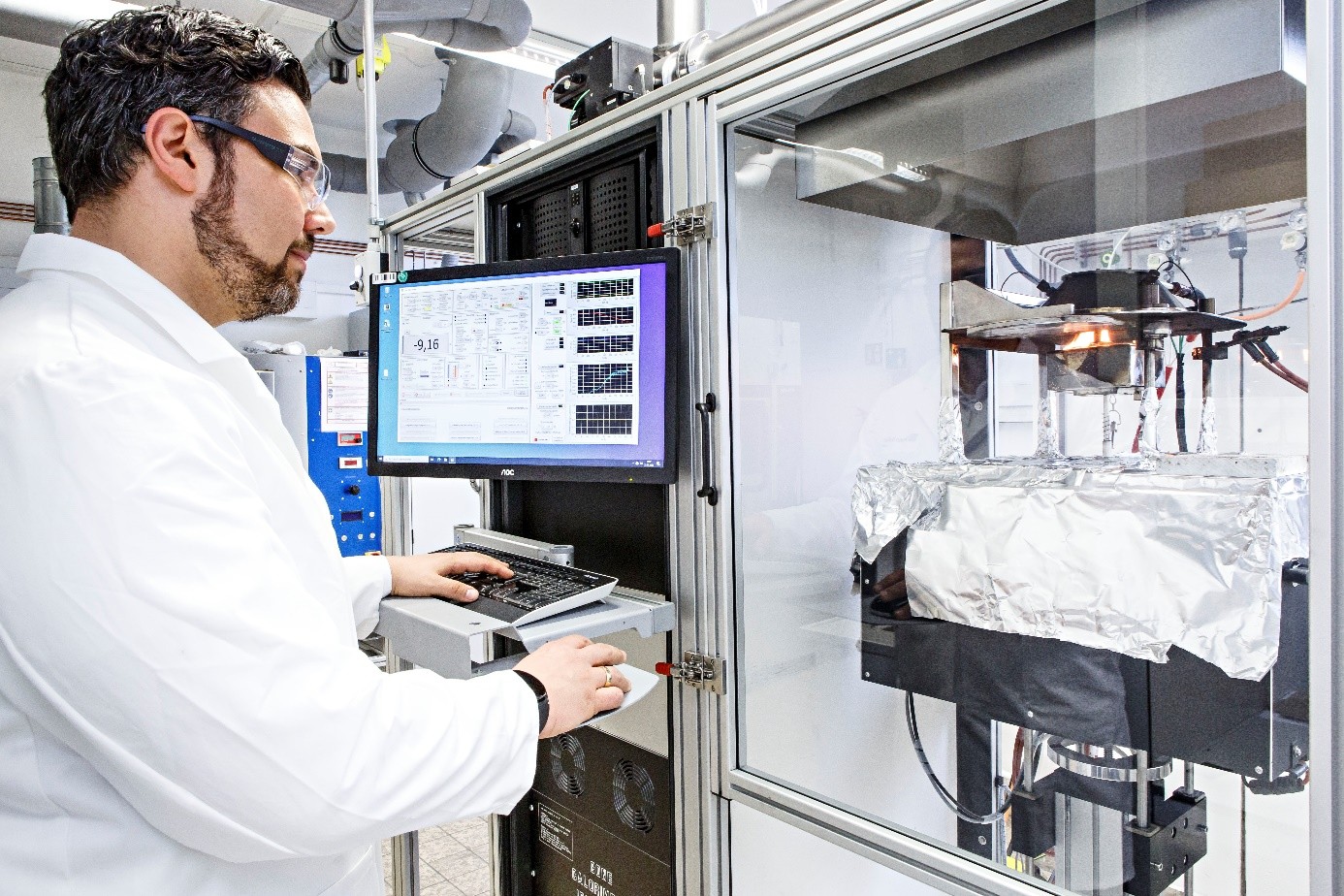
Cone calorimetry is a relative method for analyzing and comparing the forced combustion of materials. The materials are burned at different heat outputs and the released combustion heat, exhaust gases and mass changes are analyzed and recorded. This allows combustion to be tracked with time resolution and conclusions to be drawn about the selected material system and the formulation to be optimized.

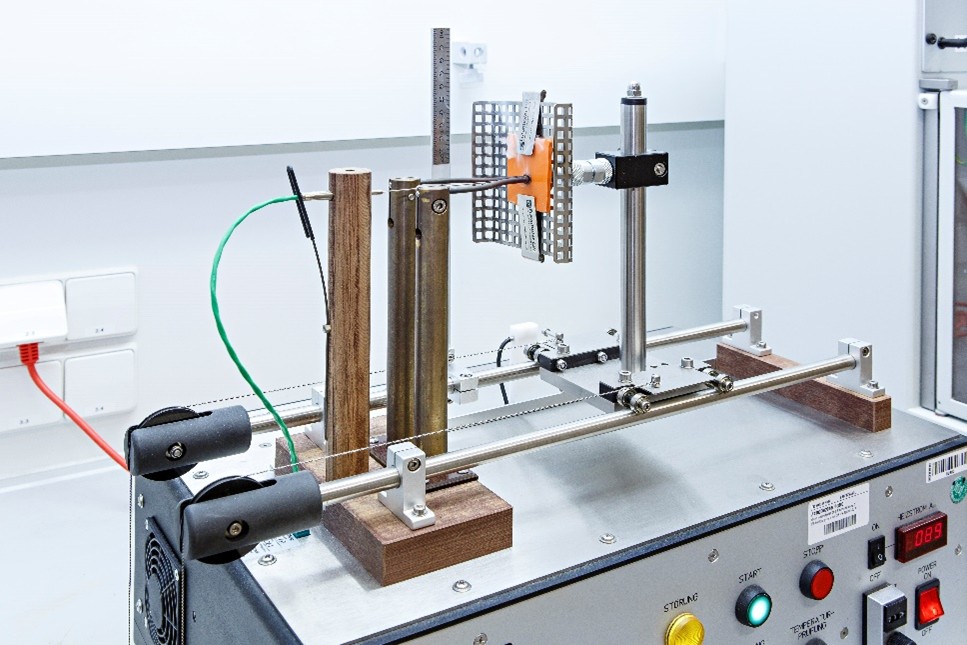
Inclined-plane tracking (IPT) can be used to determine the high-voltage strength of thermoplastics and thermosets in the voltage range of 1 kV - 5 kV (in 0.5 kV steps), which can no longer be covered by the CTI test at low voltage. For this purpose, the test specimens are exposed to a constant voltage while being dripped with an electrolyte solution. During the test, the extent of the formation of a conductive track on the polymer surface is used as the basis for evaluating the polymers. This allows polymer materials to be tested for their suitability in high-voltage applications. Test specimens measuring 130 mm x 50 mm x 6 mm are required for the tests.

The UL94 small burner test makes it possible to analyze the behavior of polymer materials (thermoplastics and thermosets) with regard to flammability and combustibility and to check the effectiveness of the formulation with little material input.