The FNR project “BioFlammschutz” has developed innovative, bio-based, and environmentally friendly phosphorus-containing flame retardants. These are intended to serve as an ecologically and economically advantageous alternative to the halogen-containing flame retardant additives currently in use, which are problematic from an ecotoxicological perspective. The new flame retardants were produced from cotton and wood cellulose and the inexpensive sugar alcohol erythritol using a method developed at Fraunhofer LBF. Their suitability was demonstrated in flame retardant applications for polyolefins and a partially bio-based polyamide.
more infoProjects
-
Components made of zinc die-cast alloys are used in various industries due to their high surface and component quality and the efficiency of the hot-chamber die-casting process. However, they are rarely used for components subject to high cyclic loads because they lack structural durabiity characteristics. To change this, the cyclic material behavior of various zinc die-cast alloys was investigated and summarized in a design concept.
more info -
Analysis of the interactions between additives and fillers using the example of flame-retardant cable sheaths
Industry Project

Flame protection of plastics by additives, layer silicates reduce the long-term stability of the cable sheathing - NanoFlame project, solutions light stabilizer and epoxy
more info -
Development of thermally conductive polymer blends
Project HEATCOP

Improve typical plastic properties by blending without reducing thermal conductivities. Thermally conductive polyamide 6 blends with high flowability.
more info -
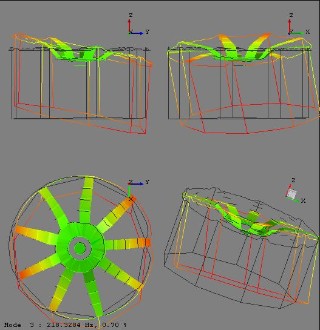
In the development process for new wheels, the structural dynamic properties are estimated by the suppliers using numerical models. To validate these properties, car manufacturers require experimental proof of these properties. For this purpose, the first newly manufactured wheels must be examined using methods of experimental structural dynamics according to special OEM specifications. Based on many years of experience, Fraunhofer LBF is familiar with these methods and the OEM's specifications. We offer wheel manufacturers the opportunity to carry out the required experiments to provide evidence.
more info -

Elastomer failure needs to be detected quickly and easily — but how? Due the variety of failure patterns that occur on elastomer components, it is not always easy to establish the exact cause of a failure. In the internal Fraunhofer project, AI Failure Analysis of Technical Elastomers, researchers are exploring the possibility of objectively analyzing elasto-mer failures through artificial intelligence. The resulting process will be transferred to customer-specific applications at a later stage.
more info -
Efficient and low-emission hybrid concepts for commercial vehicles: more range, lower total cost of ownership, compressed natural gas, validation in real-world operation.
more info -
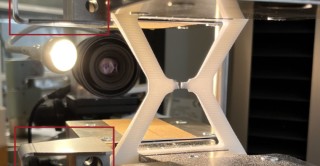
Identical parts printed in different orientations in the build space have very different mechanical properties. Knowledge of this anisotropy (directional dependence) is important for reliable simulation of components. In the AddiSim project, scientists from the Fraunhofer LBF investigated the mechanical properties of SLS printed plastic components and developed a simulation method suitable for the design.
more info -

DNAguss stands for continuous numerical design along the process chain of cast components and is an innovative research project that focuses on optimizing the design of cast components using the material EN-GJS-400-18-LT as an example. The aim of the project is to combine all software tools used during the design process of cast components into a single software chain in order to optimize castability, lightweight design and non-destructive testability while ensuring operational strength.
more info -
Technologies for rapid adaptation to changing requirements in the event of operational changes in the structural dynamic properties of mechanical systems, e.g. for intralogistics systems, machine tools, vehicles
more info

