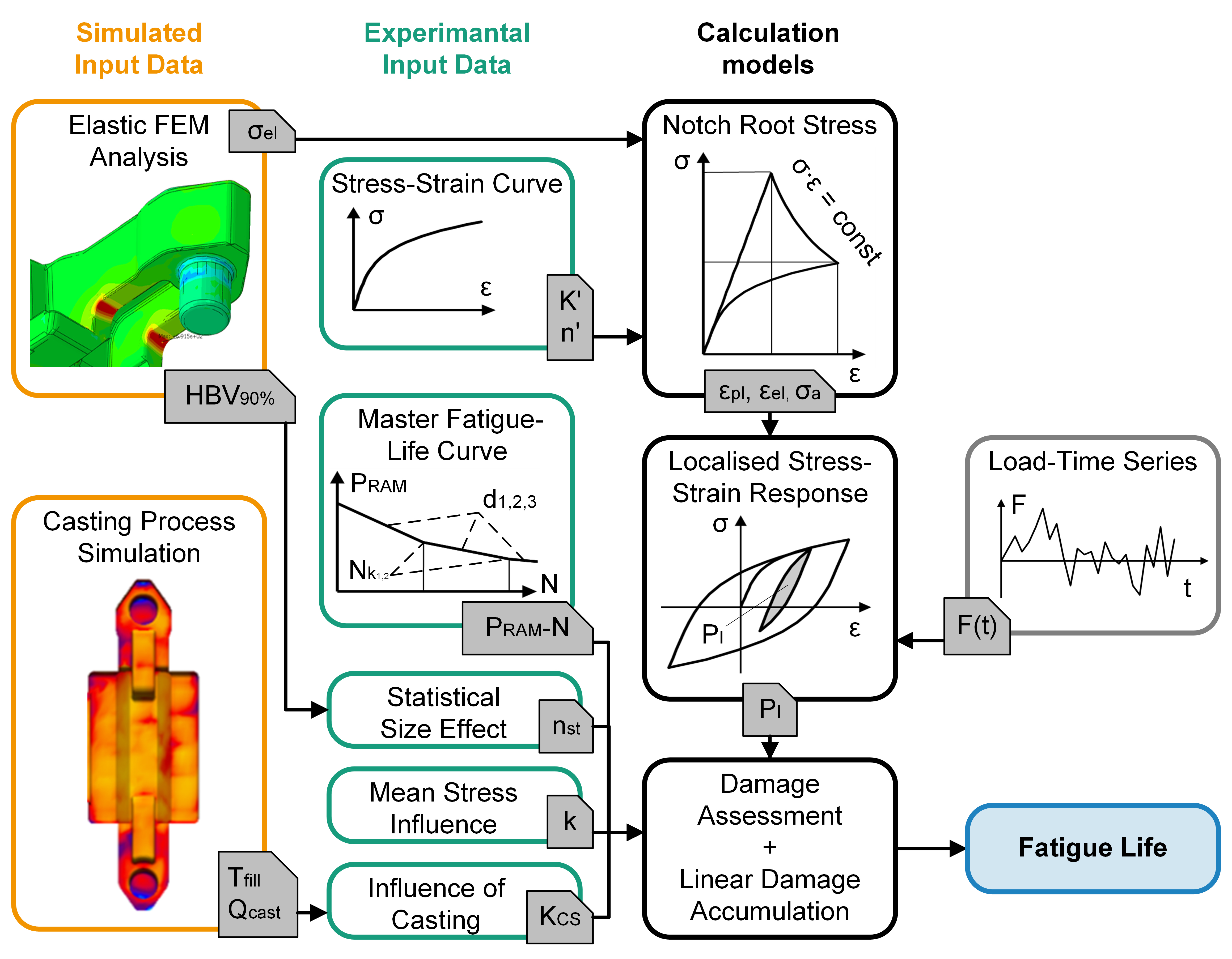
Determination of material suitability taking into account stress-mechanical, technological, and statistical size influences.
Components made of zinc die-cast alloys are used in various industries due to their high surface and component quality and the efficiency of the hot-chamber die-casting process. However, they are rarely used for components subject to high cyclic loads because they lack structural durability characteristics. To change this, the cyclic material behavior of various zinc die-cast alloys was investigated and summarized in a design concept.
Due to its short cycle times and high productivity, the hot chamber die casting process is the most important manufacturing process for zinc materials. Compared to aluminum, zinc die-cast alloys are characterized by their low melting point and the possibility of producing thin-walled castings with high surface quality and dimensional accuracy. However, zinc die-cast alloys are rarely used for components subject to high cyclic loads due to a lack of characteristic values and design methods for describing cyclic material behavior.